Overview
In electronic circuits, transistors are important switching and amplifying components and are widely used in various circuit designs. This article will briefly summarize the characteristics of NPN and PNP transistors and their applicable scenarios to help you better understand their functions and working principles.
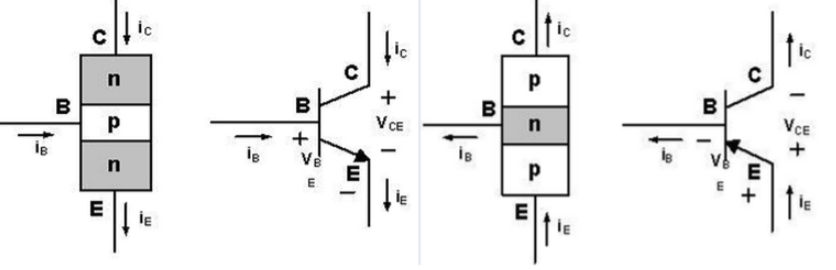
The Structure of NPN and PNP Transistors
The PN junction of an NPN transistor is located at the bottom and the emitter (E) is grounded, while the PNP transistor is the opposite, with the PN junction located at the top and the emitter (E) connected to VCC. The arrows marked indicate the direction of current flow:
- NPN: Current flows from the base (B) to the emitter (E), thereby controlling the current (Ic) from the collector (C) to the emitter.
- PNP: Current flows from the emitter (E) to the base (B), and then controls the current (Ic) from the collector (C) to the emitter.
Working Principle of Transistor
The transistor can be used as a current-controlled switch, and its working principle is as follows:
- NPN transistor:The current (Ib) from the base (B) to the emitter (E) controls the current (Ic) from the collector (C) to the emitter (E).
During normal amplification, the voltage relationship is: VC > VB > VE. - PNP transistor:The current (Ib) from the emitter (E) to the base (B) controls the current (Ic) from the emitter (E) to the collector (C).
During normal amplification, the voltage relationship is: VE > VB > VC.
The Difference between NPN and PNP
- Current direction: NPN current flows from B to E, while PNP current flows from E to B.
- Voltage polarity: NPN requires positive voltage at the base to work, while PNP requires negative voltage.
In summary, the voltage and current direction of each pole of BJT are consistent, and the current will not flow from low potential to high potential. Knowing these basic concepts, you can choose the right transistor type when designing circuits to meet different needs.
I hope this article can help you better understand the working principles and applications of NPN and PNP transistors! If you have any questions or want to discuss in depth, please contact us as follows:
Email: bella.liu@semiware.com
Tel: +86-13818226184
Whatsapp: 008613818226184


Comments (0)