📌 What is SCR and Its Working Principle?
A silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) is a commonly used power semiconductor device that can conduct and transmit high-power current when triggered by a control terminal. Its efficient switching capability and reliable control characteristics make it widely used in industrial control, power electronics, and home appliances.
Working Principle: An SCR consists of a PNPN structure, which is triggered to conduct through the gate. After conduction, it remains conductive until the current drops below the holding current before turning off.
📌 What are the Types of SCR and Applications?
1.Classification by Structure
Standard Thyristor
- Features: The most basic thyristor structure, suitable for general power switching and control applications, mainly used for rectification and voltage regulation.
- Applications: Widely used in motor drives, lighting regulation, temperature control, power supply regulation, etc. For example, in phase-controlled dimming and speed control of household appliances.
Reverse Conducting Thyristor (RCT)
- Features: Integrates a reverse diode in its structure, capable of conducting both forward and reverse currents simultaneously, eliminating the need for an additional anti-parallel diode.
- Applications: Commonly used in AC motor control, such as motor drives and rectifier circuits, eliminating the need for an external reverse diode.
Fast Switching Thyristor
- Features: Has a short turn-off time and a fast turn-on speed, suitable for applications requiring rapid switching. Its turn-off time is typically within a few microseconds, suitable for high-frequency applications.
- Applications: Commonly used in switching power supplies, frequency converters, and other circuits requiring high-frequency switching, especially in industrial control and power conversion fields.
Thyristor (Gate Turn-Off Thyristor, GTO)
- Features: A thyristor that can be turned off by gate control. Compared to ordinary thyristors, GTOs can not only be triggered to conduct but also forced to turn off by a gate signal. A large negative gate current is required for turn-off.
- Applications: Used in applications requiring turn-off capability, such as inverters, DC motor drives, adjustable power supplies, and high-voltage DC transmission.
Triac (Bidirectional Thyristor)
- Features: A triac is a bidirectional thyristor that can be controlled in AC circuits, conducting in both the positive and negative half-cycles. Its structure is essentially two SCRs connected in anti-parallel but sharing a single gate.
- Applications: Widely used in switching and regulating AC circuits, such as AC motor control, household appliance speed control, lighting adjustment, power regulation, and AC voltage regulation.
2.Classification by Function and Characteristics
Controllable SCRs
- Features: SCRs used for precise control of voltage and current. Their conduction angle can be adjusted via an external control circuit, thereby regulating output power.
- Applications: Primarily used in phase-controlled regulators, motor speed controllers, and temperature controllers.
High-Power SCRs
- Features: Designed for handling high current and high voltage, possessing extremely high power handling capacity, capable of handling thousands of amperes of current and thousands of volts of voltage.
- Applications: High-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission, high-power rectifier circuits, large industrial motor control, frequency converters, and power conversion equipment.
Low-Power SCRs
- Features: Suitable for low-voltage, low-current applications, typically used in household appliances and low-power electronic devices.
- Applications: Low-power devices such as power tools, household appliances, lighting controllers, and electronic toys.
3.Classification by Control Method
Electrically Triggered Thyristors
- Features: Thyristors that are triggered to conduct by applying current to the gate. This is the most common triggering method and is widely used in various power control applications.
- Applications: Used in most general power supply regulation, phase-controlled rectification, and power regulation applications.
Optically Triggered Thyristors
- Features: Thyristors that are triggered to conduct by an optical signal. The trigger signal is transmitted using optical fiber, enabling isolated control of high-voltage, high-power circuits.
- Applications: High-voltage, high-power power systems, such as high-voltage direct current transmission systems, industrial automation equipment, etc.
📌 How to choose SCR?
When selecting an SCR, the following factors need to be considered:
- Voltage rating (VDRM)
- Current rating (IT)
- Control method (gate or optical trigger)
- Power requirements (high power/low power)
e.g
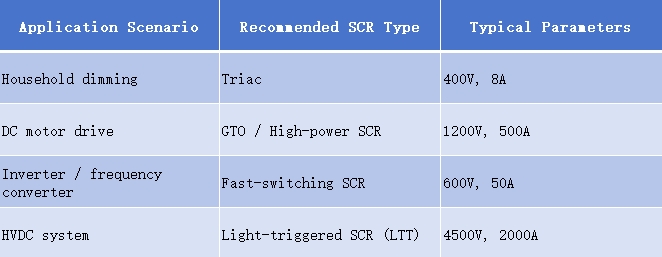
📌 SCR vs Other Power Devices
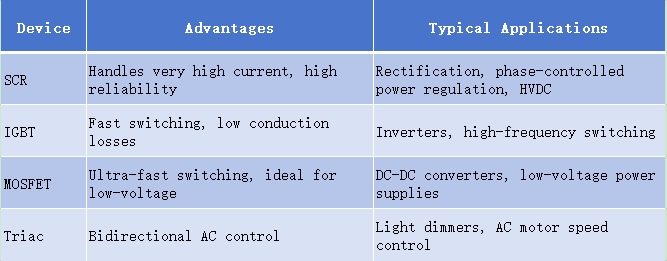
❓ FAQs
Q: What is the difference between SCR and TRIAC?
A: An SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) is a unidirectional device that only conducts current in one direction, making it suitable for DC or controlled rectification. A TRIAC, on the other hand, is a bidirectional device that can conduct in both directions, making it ideal for controlling AC power such as in dimmers or AC motor controllers. In short: SCR → one direction; TRIAC → both directions.
Q: Is thyristor the same as TRIAC?
A:A TRIAC is a type of thyristor, but not all thyristors are TRIACs. The term thyristor refers to the broader family of PNPN semiconductor switching devices, including SCRs, TRIACs, GTOs, RCTs, and others. TRIAC is specifically designed for AC switching applications and is essentially two SCRs connected in inverse parallel within one device.
Q: Is an SCR a transistor?
No. An SCR is not a transistor. An SCR is a four-layer PNPN device that provides controlled rectification and latching behavior, while a transistor is typically a three-layer device (BJT or MOSFET) designed for signal amplification or fast switching. SCRs are optimized for high-power applications and controlled conduction, while transistors are designed for amplification and high-speed switching.
Q: Can I request free samples?
A: Yes, free sample is available.
Q: What are the minimum order quantity and delivery time?
A: The MOQ is flexible, and small-batch sampling is supported initially.Regarding delivery time, items in stock can be shipped immediately; however, high-power or special specifications typically require a delivery time of 2-4 weeks.
🌏 Semiware offers a full range of SCR products, including:
- Gate-triggered SCRs
- Single-phase SCRs
- Three-quadrant/four-quadrant bidirectional SCRs
- Triacs
View details👉: Semiware SCR Product Line


Comments (0)