Overview
Thyristors and transistors are both semiconductor devices used for switching and amplification in electronic circuits, but they have key differences in their operation, applications, and characteristics. Here’s a detailed comparison:
Basic Definition
- Thyristor (SCR - Silicon Controlled Rectifier):
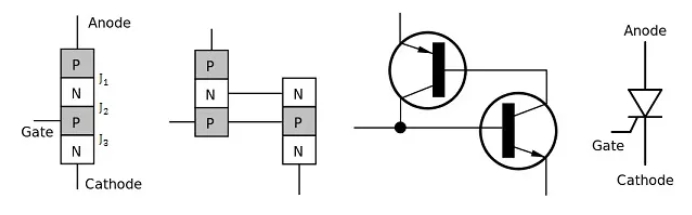
A latching semiconductor device with 4 layers (PNPN) and 3 terminals (Anode, Cathode, Gate).
Once triggered, it remains ON until the current drops below a threshold (called the holding current). - Transistor (BJT, MOSFET, IGBT, etc.):
A 3-layer (NPN or PNP for BJT) or 4-layer (for MOSFET/IGBT) device with 3 terminals (Emitter, Base, Collector for BJT; Source, Gate, Drain for MOSFET).
Can be turned ON/OFF continuously by controlling the base/gate current/voltage.
Control
- Thyristor:
Gate trigger turns it ON, but no direct turn-off control (except for GTOs - Gate Turn-Off thyristors).
Used in phase control (e.g., dimmers, motor speed control). - Transistor:
Base current (BJT) or Gate voltage (MOSFET/IGBT) controls conduction.
Can be PWM-controlled for variable switching.
Switching Speed
- Thyristor: Slower switching; not suitable for high-frequency applications.
- Transistor: Much faster switching; ideal for digital circuits and high-frequency applications
Power Handling & Efficiency
Thyristor:
- Better for high voltage/current (kV & kA ranges).
- Lower conduction losses (better for AC power control).
- Not suitable for high-frequency switching.
Transistor (MOSFET/IGBT):
- Better for high-frequency switching (kHz to MHz).
- More efficient in switched-mode power supplies (SMPS).
- Lower power handling than thyristors (but IGBTs bridge the gap).
Applications
Thyristor:
- AC power control (light dimmers, motor speed control)
- Controlled rectifiers
- High-voltage DC transmission
Transistor:
- Signal amplification (BJTs, FETs)
- Switching in logic circuits, SMPS, audio systems
- Microcontrollers, computers
Conclusion
- Use a thyristor for high-power AC switching where latching behavior is acceptable.
- Use a transistor for fast switching, amplification, or DC applications requiring active control.
About Semiware
Semiware has a comprehensive product lineup of circuit protection device products. The company leverages its technology in the semiconductor field and application background in end products to serve customers in the electronics, automotive and industrial markets. For more information, please visit semiware official website: https://en.semiware.com/


Comments (0)